Mini
[알고리즘] 백준 1062 가르침 // 조합, 비트마스킹, 백트래킹 본문
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1062
* 내 풀이
- 최초풀이 : 막구현 -> 26C13 (최악의경우) = 1천만 -> 시초
- a,n,t,i,c는 무조건 뽑아야함 -> 미리선택, 비트켜기
입력:
N, K 입력받기
N개의 단어 입력받아 arr에 저장
필수 처리:
if K < 5: return 0
초기화:
bit = 0
'a','n','t','i','c' 위치의 비트 켜기
비트마스크로 알파벳 선택:
for subset in 1 to (1<<26)-1:
if 필수알파벳 미포함: continue
if 선택된 알파벳 개수 != K: continue
선택된 알파벳으로 단어 읽기 체크:
cnt = 0
for 각 단어:
if 모든 문자를 읽을 수 있음:
cnt++
ret = max(ret, cnt)
출력:
ret 출력#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int n,k,ret;
int study[26];
vector<string> arr;
void go(int subset) {
memset(study,0,sizeof(study));
for(int i=0;i<26;++i) {
if(subset & (1<<i)) {
study[i]=1; //0:'a', 1:'b'
}
}
int cnt=0;
for(auto s : arr) {
bool flag=true;
for(auto c: s) {
if(!study[c-'a']) {
flag=false;
break;
}
}
if(flag) cnt++;
}
ret=max(ret,cnt);
}
void combi(int idx, vector<int> v) {
if(v.size()==k) {
memset(study,0,sizeof(study));
for(auto i : v) {
study[i]=1; //0:'a', 1:'b'
}
int cnt=0;
for(auto s : arr) {
bool flag=true;
for(auto c: s) {
if(!study[c-'a']) {
flag=false;
break;
}
}
if(flag) cnt++;
}
ret=max(ret,cnt);
return; //return 빼먹지마
}
for(int i=idx+1;i<26;++i) { //idx+1 부터!
v.push_back(i);
combi(i,v);
v.pop_back();
}
}
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin>>n>>k;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i) {
string s;
cin>>s;
arr.push_back(s);
}
// k가 5보다 작으면 'a','n','t','i','c'도 읽을 수 없음
if(k < 5) {
cout << 0;
return 0;
}
// 필수 알파벳 5개를 뺀 나머지 k-5개를 선택
//k -= 5;
//'a','n','t','i','c' 는 기본으로
int bit=0;
for(char c : {'a','n','t','i','c'}) {
study[c-'a'] = true;
bit |= (1<<(c-'a')); // c-'a' 아님에 주의!, 비트를 켜야함
}
// vector<int> v;
// combi(-1,v);
for(int subset = 1; subset < (1<<26); ++subset) {
//subset|=bit; // 필수포함 알파벳, 이러면 안됨
// 필수 알파벳이 포함되어 있는지 확인
if((subset & bit) != bit) continue;
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<26;++i) {
if(subset & (1<<i)) {
cnt++;
}
}
//nCk
if(cnt==k) {
go(subset);
}
}
cout<<ret;
return 0;
}- 내풀이도 통과함
- if(subset & bit) != bit continue에서 가지치기역할을 하고있음!
* 큰돌 풀이
- abcdef.... 알파벳을 선택 하고 안하고 O, X 기반으로 시작 (2^26)
- words 에 단어들의 비트를 저장하는 특징 => 읽을수있는지 쉽게검사
- dfs(index, 배워야할 알파벳수, visited대신 mask에 현재 상태 저장)

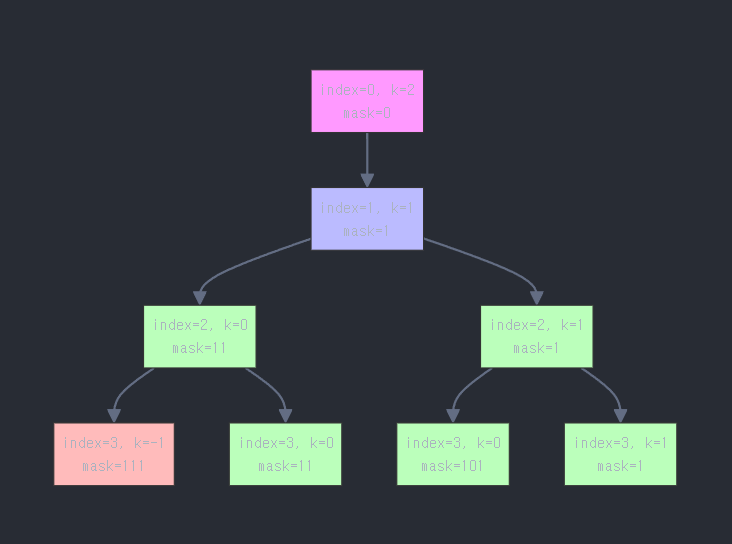
- 이때, 무작정 O ,X로 완탐을한다면 시간초과
- 필수알파벳은 무조권 배워야함-> 배우지않는경우는 가지치기해야 시간내에 풀이된다.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int n,k,ret;
int study[26];
int words[54]; // 단어를 bit로 나타내어 저장
vector<string> arr;
// mask: 현재 배운 알파벳들의 비트마스크
// 현재 배운 알파벳들로 읽을 수 있는 단어의 개수를 반환
int count(int mask) {
int cnt=0;
for(auto word : words) {
// word가 0이 아니고(빈 단어가 아님)
// word의 모든 알파벳이 mask에 포함되어 있으면 카운트
/**
*'abc'의 비트마스크(word) 만들기:
a: 1<<0 = 000...000001
b: 1<<1 = 000...000010
c: 1<<2 = 000...000100
word = 000...000111 (이진수로 7)
케이스별로 살펴보기:
1. mask가 "abc"인 경우:
mask = 000...000111
word = 000...000111
word & mask = 000...000111 (== word, 읽기 가능!)
2. mask가 "ab"인 경우:
mask = 000...000011
word = 000...000111
word & mask = 000...000011 (!= word, 읽기 불가능)
3. mask가 "abcd"인 경우:
mask = 000...001111
word = 000...000111
word & mask = 000...000111 (== word, 읽기 가능!)
즉, mask가 더 큰 범위면 가능!
*/
if(word && (word & mask) == word) cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
// index: 현재 검사중인 알파벳 (0: 'a', 1: 'b', ...)
// k: 앞으로 배워야 할 알파벳 수
// mask: 지금까지 배운 알파벳들의 비트마스크
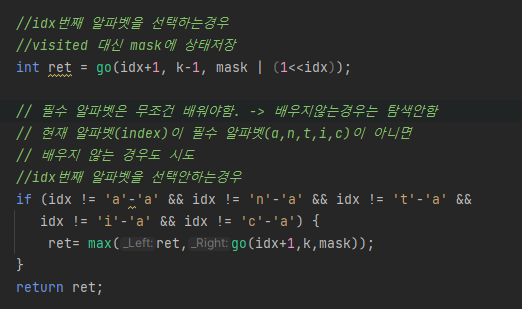
int go(int idx, int k, int mask) {
if(k<0) {
return 0;
}
if(idx==26) return count(mask);
//idx번째 알파벳을 선택하는경우
//visited 대신 mask에 상태저장
int ret = go(idx+1, k-1, mask | (1<<idx));
// 현재 알파벳(index)이 필수 알파벳(a,n,t,i,c)이 아니면
// 배우지 않는 경우도 시도
//idx번째 알파벳을 선택안하는경우
if (idx != 'a'-'a' && idx != 'n'-'a' && idx != 't'-'a' &&
idx != 'i'-'a' && idx != 'c'-'a') {
ret= max(ret,go(idx+1,k,mask));
}
return ret;
}
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin>>n>>k;
// 단어를 bit로 나타내어 저장 => 나중에 체크쉬움
/**
* 예를 들어 단어가 "ant"라면:
1. 'a': 1 << (97-97) = 1 << 0 = 000...0001
2. 'n': 1 << (110-97) = 1 << 13 = 0010000000000
3. 't': 1 << (116-97) = 1 << 19 = 1000000000000000000
OR 연산(|=)으로 합치면:
word[i] = 1000000000010000000001
이렇게 하나의 정수에 해당 단어에 포함된 모든 알파벳의 위치에 1이 설정
*/
for(int i=0;i<n;++i) {
string s;
cin>>s;
for(auto c:s) {
words[i]|=1<<(c-'a');
}
}
// 첫 알파벳부터, k개를 배워야함, 아직 아무것도 배우지 않은 상태에서 시작
cout<<go(0,k,0);
return 0;
}
'Algorithm > 비트마스킹' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알고리즘] 백준 14391 종이조각 // 비트마스킹, 1차원을 2차원으로 바꾸는힘 (0) | 2025.01.16 |
|---|---|
| [알고리즘] 백준 2234 성곽 // 비트마스킹, vis의 값에 의미를 부여하라, i번째 비트끄기 (0) | 2025.01.12 |
| [알고리즘] 백준 1987 알파벳 // 비트마스킹, i번째 비트켜짐확인, vis를 숫자1개로 나타내는 힘 (0) | 2025.01.11 |
| [알고리즘] 백준 19942 다이어트 // 비트마스킹, 1-idx (0) | 2025.01.11 |
| [알고리즘] 백준 17471 게리멘더링 // 비트마스킹, dfs 구역체크는 노드1곳에서 시작 (0) | 2025.01.08 |




